As automotive professionals, it is crucial to have a comprehensive understanding of the various fluids that play a vital role in the functioning of vehicles. One such fluid is coolant, which is responsible for regulating engine temperature and preventing overheating. What’s most important to know is that coolant is not immune to breakdown or degradation over time.
Understanding Coolant Breakdown
Coolant, a mixture of ethylene glycol or propylene glycol and water, is designed to maintain stable engine temperatures in both extreme heat and cold conditions. Over time, however, the coolant can deteriorate, leading to a loss of its essential properties and diminished performance. The breakdown of coolant typically occurs due to the following factors:
- Oxidation: Coolant is exposed to oxygen from the atmosphere, which can cause oxidation. Oxidation results in the formation of acids, sludge, and contaminants that compromise the coolant’s effectiveness.
- Contamination: External factors such as dirt, debris, and engine oil leaks can contaminate the coolant. Contaminants can disrupt the fluid’s chemical balance and reduce its ability to transfer heat efficiently.
- Corrosion: The coolant comes into contact with various metals within the engine, including aluminum, steel, and copper. Over time, the coolant’s corrosive elements can cause rust, scale, and deposits, affecting the cooling system’s overall performance.
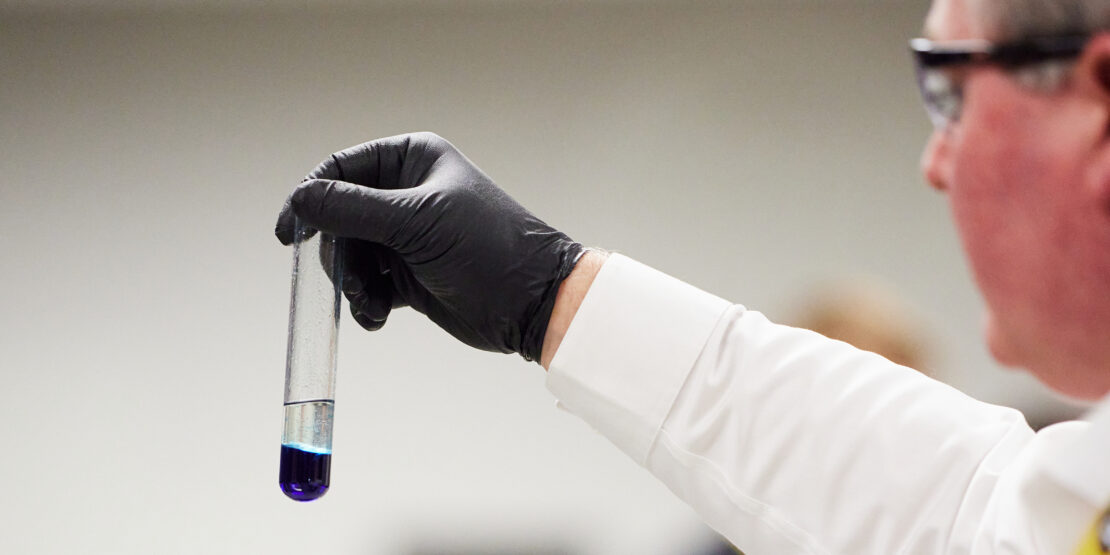

Consequences of Coolant Breakdown
To encourage vehicle owners to schedule regular cooling system maintenance, it is important to educate them about the consequences of coolant breakdown. Failure to address coolant breakdown can have severe consequences for a vehicle’s engine and overall performance. Some of the potential repercussions include:
- Overheating: Deteriorated coolant loses its ability to dissipate heat effectively. This can lead to engine overheating, potentially causing irreversible damage to critical engine components.
- Reduced Lubrication: Coolant breakdown can also compromise the lubricating properties of the fluid. Insufficient lubrication increases friction and wear on engine parts, leading to premature failure.
- Corrosion Damage: Corrosive elements in degraded coolant can corrode metal surfaces, leading to the formation of rust and deposits in the cooling system. This can restrict coolant flow, impair heat transfer, and damage crucial engine components.
Preventing Coolant Breakdown
Proactive maintenance practices can significantly mitigate coolant breakdown and ensure optimal performance. Here are some essential preventive measures:
- Regular Coolant Inspections: Schedule periodic coolant inspections to assess its condition, pH level, and freeze point. This allows early detection of any signs of degradation, contamination, or pH imbalance.
- Coolant Replacement: Regular coolant replacement, as recommended by the vehicle manufacturer, helps remove accumulated contaminants and maintain the fluid’s effectiveness.
- Correct Coolant Type: Use the coolant specified by the vehicle manufacturer to ensure compatibility with the engine’s materials. Different engines may require specific coolant formulations to prevent corrosion or other issues.
- Address Leaks Promptly: Any coolant leaks should be identified and repaired promptly. Leaks not only lead to coolant loss but also introduce contaminants into the system.
- Cooling System Maintenance: Regularly inspect and maintain the cooling system components, including radiator, hoses, thermostat, and water pump, to ensure they are functioning correctly and are free from obstructions.

If you’re an automotive professional, understanding the inevitable breakdown of coolant is crucial. By understanding what causes coolant breakdown, its consequences, and taking preventive measures, you can stay one step ahead of the game. This means tackling issues head-on and extending the cooling system’s lifespan, which will not only make your customers happy, they will trust you even more.